Influenza (Flu) in Children
- Home
- Influenza (Flu) in Children
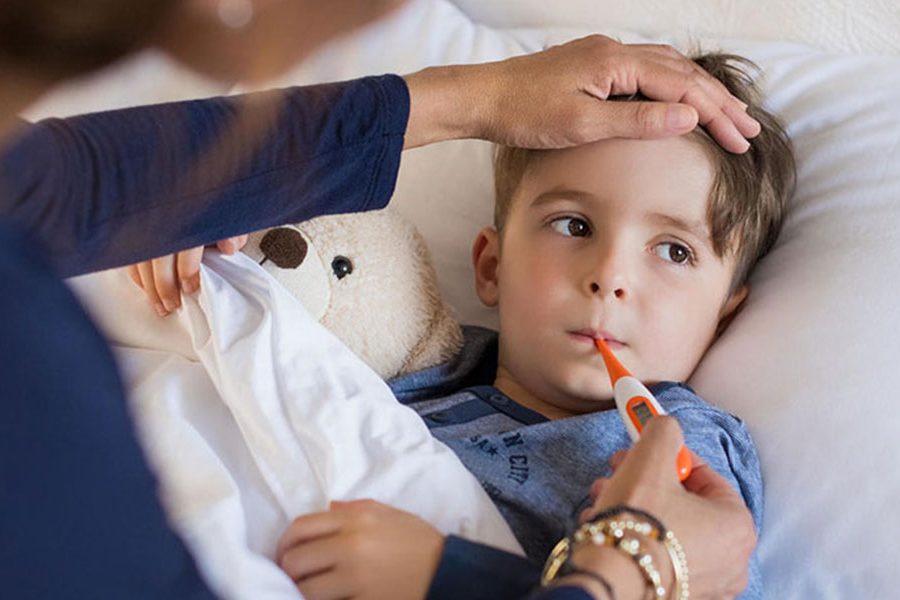

In this article, you can find answers to questions such as "What is flu?", "How is influenza treated in children?", "What are the symptoms of influenza?", and what you need to know about the flu vaccine, which is frequently seen especially in winter months.
With the arrival of winter, flu cases increase and are common in schools. Influenza (flu) virus is transmitted through droplets (coughing, sneezing) or by touching contaminated surfaces. Therefore, when coughing or sneezing, we should cough into a tissue or elbow. We must contaminate every place we touch with the viruses that infect our hands. The flu usually clears up on its own, but it can make some people seriously ill. It is very important to get a flu vaccine if it is recommended by experts.
What Are The Symptoms of Flu?
Flu symptoms appear very quickly and may include:
- Sudden fever
- Body pain
- Feeling tired or exhausted
- Dry cough
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea or abdominal pain
- Feeling sick
When Should We Suspect Flu in Children?
Sudden onset of high and persistent fever, sore throat, headache, cough, widespread muscle and joint pain, vomiting and diarrhea may occur in children. Influenza should be considered in young children, especially if persistent fever and malaise are prominent. Influenza virus can cause pneumonia. Another complication due to influenza is muscle inflammation. In this case, the child may feel so much pain that he cannot stand or have difficulty walking, and muscle inflammation is diagnosed with the increase of an enzyme called creatine kinase in the blood.
What are the Differences Between Cold and Flu?
The main differences between cold and flu (influenza) are:
- Cold and flu symptoms are similar, but flu symptoms tend to be more severe.
- While the flu occurs rapidly within a few hours, the common cold progresses slowly.
- While the flu affects more than just your nose and throat, a cold mainly affects your nose and throat.
- Flu leaves you feeling exhausted and unable to continue your daily life normally. You won't feel well when you have a cold, but you won't be so bad that you can't do your normal activities.
What is Flu Treatment?
If you get the flu, there are some things you can do to help you recover faster. These;
- Rest and sleep
- Keeping yourself warm
- Taking paracetamol or ibuprofen to reduce your fever and treat your pain.
- Drinking plenty of water to prevent dehydration (Your urine should be light yellow or clear)
Apart from this, specific antiviral drugs, symptomatic treatment for complaints and supportive treatment are recommended in the treatment. Treatment is carried out with antipyretics, rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and consuming foods rich in vitamin C.
In the home environment, rooms should be ventilated frequently and closed environments should be avoided as much as possible.
Can Flu Be Treated with Antibiotics?
Many mild bacterial infections get better on their own without antibiotics. Antibiotics do not work for viral infections such as colds and flu. Antibiotics are no longer routinely used to treat some diseases. Doctors' advice should be followed as to whether antibiotics are needed. Antibiotic resistance is a huge problem. Using antibiotics when they are not needed may cause them to stop working in the future when they are actually needed.
In Which Circumstances Should You Seek Medical Assistance in Suspicion of Flu?
If you or your child has flu symptoms and:
- If you are worried about your baby or child's symptoms,
- If you are 65 or older,
- If you are pregnant,
- You have a chronic illness or long-standing medical condition (for example, diabetes or a condition that affects your heart, lungs, kidneys, brain or nerves).
- If you have a weakened immune system (for example, due to chemotherapy or HIV),
- If your symptoms have not improved after 7 days, you should seek medical help.
In the following cases, the emergency call center must be called!
- Sudden chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Starting to cough up blood
How to Prevent the Spread of Flu?
The flu is highly contagious and can spread easily to other people. You are more likely to transmit the flu to others in the first 5 days. Flu is transmitted by germs spread through coughs and sneezes and can survive on both hands and surfaces for up to 24 hours.
To reduce the risk of contracting the flu:
- Wash your hands frequently with warm water and soap.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing.
- Throw away used tissues as quickly as possible.
- If you have a high fever or do not feel well enough to do your daily activities, try to stay home and avoid contact with other people as much as possible.
Is there an Influenza Test?
In case of clinical suspicion, it is recommended to perform a rapid influenza test by taking a nasal swab. While positive results establish a diagnosis, negative results do not definitively exclude the disease.
When to Get the Flu Vaccination?
Flu vaccines are very safe and effective. Vaccines are offered to the public each year to help protect people at risk of flu complications.
The best time to get a flu vaccine is in the fall before the flu starts to spread, but you can also get vaccinated at a later time.
Who Should Get the Flu Vaccination?
Recommended flu vaccinations for adults include:
- Those aged 50 and over.
- Those with certain health conditions.
- Pregnant women.
- Those in long-term residential care.
- Those who care for an elderly or disabled person who may be at risk if they become ill.
- People who live with someone who is more likely to get a serious infection due to a weakened immune system, such as those living with HIV, those who have had an organ transplant, or those receiving certain treatments for cancer, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Should the Flu Vaccination be Required?
It is recommended that people in the risk group defined by the Ministry of Health get the flu vaccine. Flu vaccine should not be given to people who are allergic to eggs or who have previously developed serious allergies to the ingredients contained in the vaccine.
 What is Endometriosis (Chocolate Cyst)? What are the symptoms? How to Treat?
What is Endometriosis (Chocolate Cyst)? What are the symptoms? How to Treat?  Colon Cancer (Symptoms, Stages, Treatment)
Colon Cancer (Symptoms, Stages, Treatment)  Influenza (Flu) in Children
Influenza (Flu) in Children  Stomach Cancer Symptoms and Treatment Methods
Stomach Cancer Symptoms and Treatment Methods  What is Lymph Node Swelling? What Are The Reasons?
What is Lymph Node Swelling? What Are The Reasons?  When to Use Antibiotics? What are the side effects? What is Antibiotic Resistance?
When to Use Antibiotics? What are the side effects? What is Antibiotic Resistance?  What is Muscle Spasm?
What is Muscle Spasm?  What is MRI? How to Take an MRI with Medication? Is It Harmful?
What is MRI? How to Take an MRI with Medication? Is It Harmful?  What are the Causes of Diarrhea and Vomiting? How to Treat?
What are the Causes of Diarrhea and Vomiting? How to Treat?  What is Heart Failure? What are its stages? How to Treat?
What is Heart Failure? What are its stages? How to Treat?
