Colon Cancer (Symptoms, Stages, Treatment)
- Home
- Colon Cancer (Symptoms, Stages, Treatment)
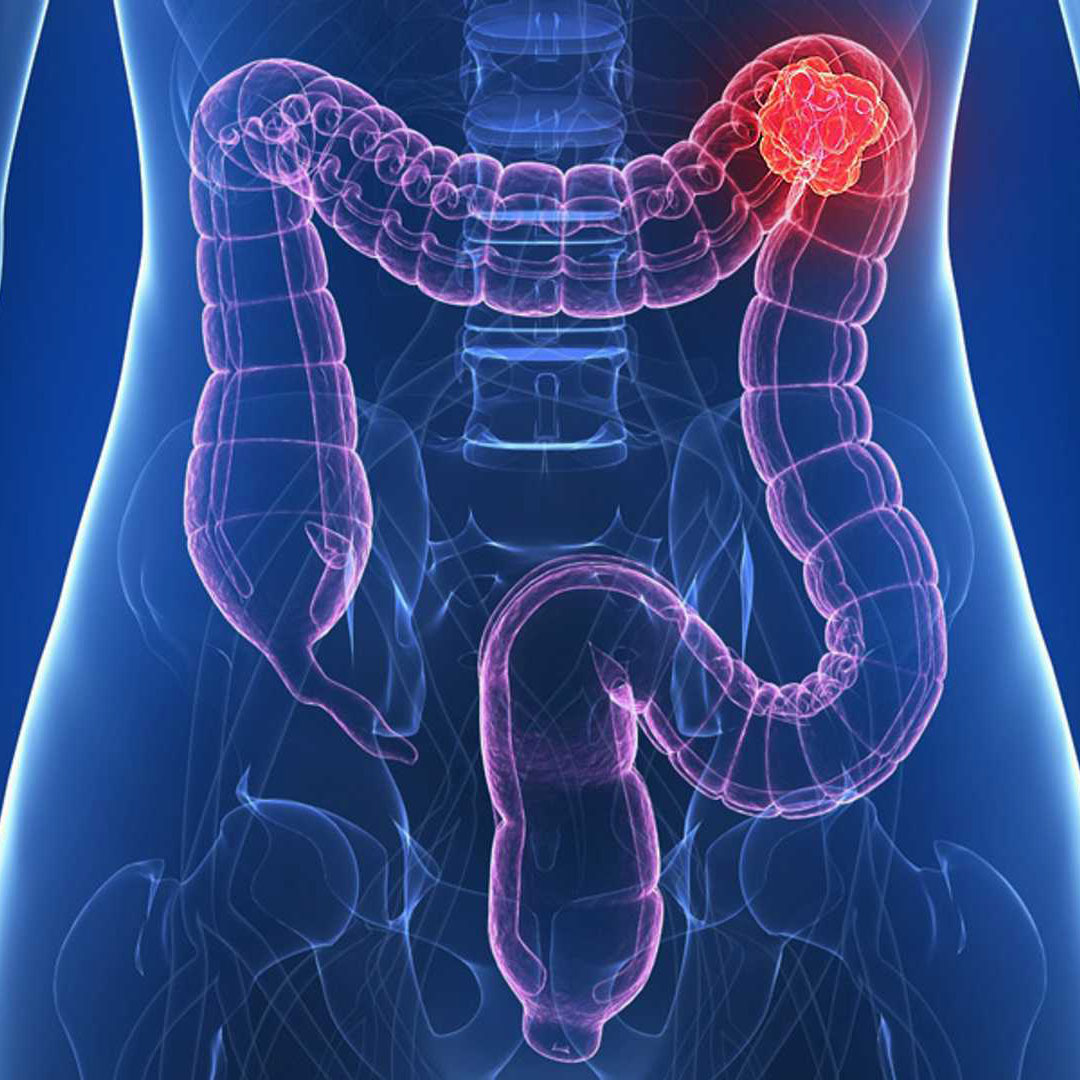
Colorectal cancer is a type of cancer originating from the cells in the inner part of the large intestine, which is the last part of the intestines.
The last 15 cm of the large intestine is called the rectum. Almost all colon cancers arise from what we call benign polyps. Therefore, finding and removing these polyps with endoscopy will reduce the risk of developing colon cancer.
Colon cancer, like other types of cancer, is divided into stages in order to determine the development and progression of the disease.
How Many Stages Does Colon Cancer Consist of?
Colon cancers are roughly examined in four stages. When caught in the early stages, the results are extremely good. Although the cause is not always clear, some conditions increase the risk of development.
What are the factors that increase the risk of large intestine cancer?
There are many factors that increase the risk of cancer types. We can list the risk factors that increase colon cancer as follows:
- Consuming foods rich in animal fat, animal protein and low in fiber,
- The disease that occurs in the form of many (sometimes hundreds) benign polyps in the large intestine, known as familial adenomatous polyposis,
- Patients with ulcerative colitis, a disease that causes ulcers on the inner surface of the large intestine,
- Those with a family history of colon cancer (mother, father and siblings).
What are the symptoms of large intestine cancer?
There are many symptoms that colorectal cancer causes in the body.
These:
Patients with ulcerative colitis, a disease that causes ulcers on the inner surface of the large intestine,
Those with a family history of colon cancer (mother, father and siblings).
What are the symptoms of large intestine cancer?
There are many symptoms that colorectal cancer causes in the body.
These:
- Blood in stool,
- Constipation or diarrhea lasting more than two weeks
- Weight loss,
- Stomach ache,
- Swelling in the abdomen,
- Weakness and fatigue,
- Lack of complete relief after defecation and the need to defecate again after a while,
- It is a change in defecation habits.
What are the Treatment Methods for Colon Cancer?
There are three main treatment methods for colon cancer.
These:
- Surgical method,
- Chemotherapy,
- It is radiotherapy.
Surgical Method in the Treatment of Colon Cancer
Surgical method is the most important and main treatment method. Sometimes alone is enough. The tumor is removed along with sufficient healthy tissue and lymph nodes around it. It is also possible for these surgeries to be performed in some patients by laparoscopic methods, known as closed surgery.
Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Colon Cancer
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment. It is usually given to patients who are microscopically likely to have cancer cells outside the large intestine after surgical treatment.
Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Colon Cancer
Radiotherapy is a form of radiation therapy. Tumor cells are eliminated with high-energy rays (radiation). It is generally used in cancers of the rectum, which is the last part of the large intestine. It is sometimes used before surgery and sometimes after surgery.
 What is Endometriosis (Chocolate Cyst)? What are the symptoms? How to Treat?
What is Endometriosis (Chocolate Cyst)? What are the symptoms? How to Treat?  Colon Cancer (Symptoms, Stages, Treatment)
Colon Cancer (Symptoms, Stages, Treatment)  Influenza (Flu) in Children
Influenza (Flu) in Children  Stomach Cancer Symptoms and Treatment Methods
Stomach Cancer Symptoms and Treatment Methods  What is Lymph Node Swelling? What Are The Reasons?
What is Lymph Node Swelling? What Are The Reasons?  When to Use Antibiotics? What are the side effects? What is Antibiotic Resistance?
When to Use Antibiotics? What are the side effects? What is Antibiotic Resistance?  What is Muscle Spasm?
What is Muscle Spasm?  What is MRI? How to Take an MRI with Medication? Is It Harmful?
What is MRI? How to Take an MRI with Medication? Is It Harmful?  What are the Causes of Diarrhea and Vomiting? How to Treat?
What are the Causes of Diarrhea and Vomiting? How to Treat?  What is Heart Failure? What are its stages? How to Treat?
What is Heart Failure? What are its stages? How to Treat?
